Comparing 4 vendors in Thermoelectric Generators Startups across 0 criteria.
Thermoelectric generators (TEG) are solid-state devices that convert heat into electricity. They are based on the Seebeck effect, which produces an electric current when dissimilar metals are exposed to varying temperatures. Thermoelectric generators have p-type and n-type elements through which the electrons migrate and, as a result, generate electric current. These generators are a renewable energy source and are easy to install, safe to store, cost-effective, and low-maintenance products. Thermoelectric generators are used for power generation across automotive & transportation, aerospace & defense, marine, industrial, consumer, medical, oil & gas, and telecommunication sectors.
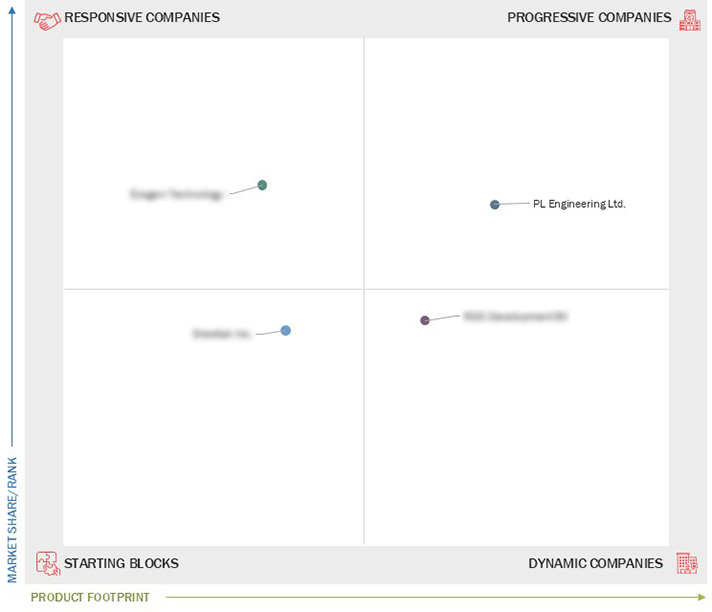
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 High demand for waste heat recovery and direct power generation
2.2.1.2 Need for fuel efficiency amid stringent emission control norms
2.2.1.3 Durable and maintenance-free power source
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Low efficiency of thermoelectric generators
2.2.2.2 High initial cost and lack of skilled personnel
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Ongoing research and development to enhance performance
2.2.3.2 Increase adoption of thermoelectric generators across various sectors
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Availability of prominent substitutes and structural complexities
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.3 Coherent Corporation
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Product Launches
3.8.2 Acquisitions
3.8.3 Partnerships, Collaborations, Alliances and Joint ventures
4.1 Ecogen Technology
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 PL Engineering Ltd.
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 RGS DEVELOPMENT BV
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 Sheetak Inc
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments

 einpresswire
einpresswire
 Dec 2025
Dec 2025

