Comparing 11 vendors in Battery Swapping Startups across 0 criteria.
According to Autotrader (UK), battery swapping involves switching out a depleted electric vehicle battery with a fully charged one rather than plugging it in to charge. The process usually takes under five minutes, which is useful for electric vehicle (EV) owners when compared to a 30-minute wait or more at a typical recharging station. The battery swapping process involves driving an EV to a battery swapping station, and the station does the rest of the work, including lifting the vehicle, removing the bolts for the chassis and battery, and then replacing the empty battery, all completely autonomously.
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Rise in investments in battery swapping infrastructure by OEMs
2.2.1.2 Lower initial purchase cost of electric vehicles due to battery swapping
2.2.1.3 Reduced charging time
2.2.1.4 Increasing government initiatives and investments in battery swapping
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Lack of standardization of batteries used in different vehicles
2.2.2.2 Limited vehicle compatibility
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Introduction of innovative modular battery swapping solutions
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Battery ownership and business model challenges
2.2.4.2 Battery degradation & lifecycle management
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
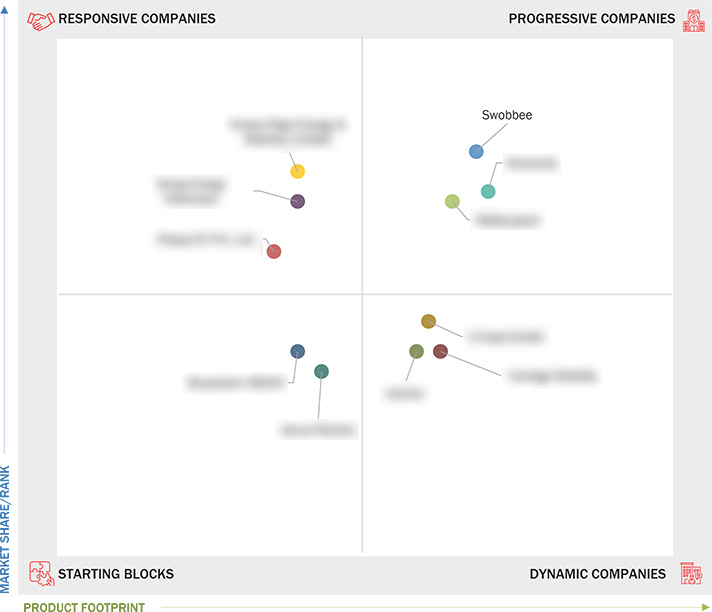
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Deals
3.8.2 Expansions
3.8.3 Others
4.1 Swobbee
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 Swobbee
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 Batterypool
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 Amara Raja Energy & Mobility Limited
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 Swap Energi Indonesia
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 Okaya EV Pvt. Ltd.
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 Kooroo
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 E-Hual GmbH
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments
4.9 Contigo Mobility
4.9.1 Business overview
4.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.9.3 Recent developments
4.10 Blueshark ASEAN
4.10.1 Business overview
4.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.10.3 Recent developments
4.11 Janus Electric
4.11.1 Business overview
4.11.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.11.3 Recent developments

 einpresswire
einpresswire
 Dec 2025
Dec 2025

