Comparing 10 vendors in Natural Fiber Composites Startups across 0 criteria.
Natural fiber composites, made from fibers like flax, kenaf, and hemp combined with thermoplastic or thermoset resins, are used in automotive, building, and construction industries. Flax fibers are favored for their high abrasion resistance, impact strength, and biodegradability. The market is growing due to demand for lightweight, fuel-efficient vehicles and sustainable buildings. The flax fiber segment dominates due to its superior properties, while PP resin is highly demanded for its excellent characteristics. Compression molding is the leading manufacturing process, and the automotive industry is the largest end-use segment. Europe leads the market, driven by established automobile manufacturers and government regulations promoting eco-friendly materials.
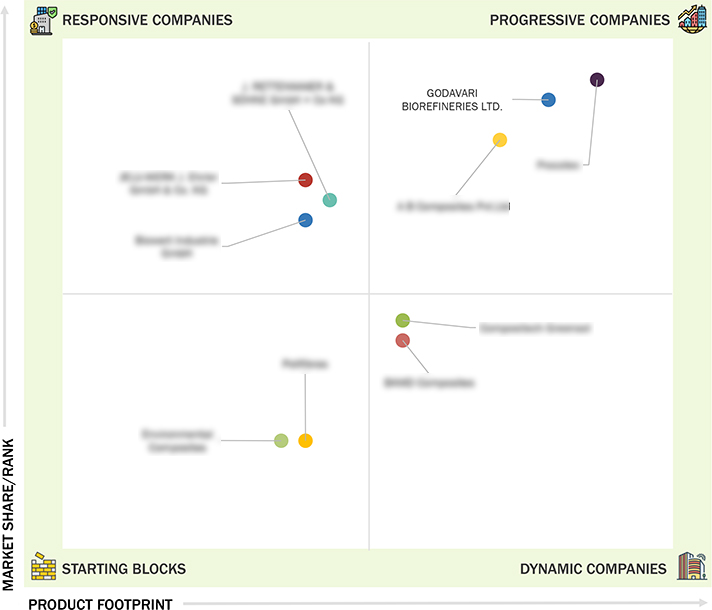
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Increasing demand for lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicles
2.2.1.2 Growing government regulations regarding environmentally friendly materials
2.2.1.3 Recyclability and sustainability
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Lower durability compared to synthetic fiber composites
2.2.2.2 Fluctuating costs, availability, and quality of raw materials
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Growing use of natural fiber composites for household furniture
2.2.3.2 Increasing adoption of 3D printing for manufacturing natural fiber composites
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Low thermal stability and high moisture absorption
2.2.4.2 Dominance of glass fiber composites
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Deals
4.1 Procotex
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 GODAVARI BIOREFINERIES LTD
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 A B Composites Pvt.Ltd
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 JELU-WERK J. Ehrler GmbH & Co. KG
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 J. RETTENMAIER & SÖHNE GmbH + Co KG
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 Biowert Industrie GmbH
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 Compositech Greensol
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 BAMD Composites
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments
4.9 Polifibras
4.9.1 Business overview
4.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.9.3 Recent developments
4.10 Environmental Composites
4.10.1 Business overview
4.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.10.3 Recent developments

 Indianchemicalnews.com
Indianchemicalnews.com
 Feb 2026
Feb 2026

