Comparing 7 vendors in Pharmacy Automation Startups across 0 criteria.
Pharmacy automation refers to using technology & automated systems to manage and streamline medication dispensing, packaging, inventory control, and other pharmacy-related tasks. It enhances efficiency, reduces human errors, ensures compliance with regulatory standards, and improves patient safety. The key automation solutions include robotic dispensing systems, automated medication storage, and workflow management software. These technologies are widely adopted in hospitals, retail pharmacies, and long-term care facilities to optimize pharmaceutical operations.
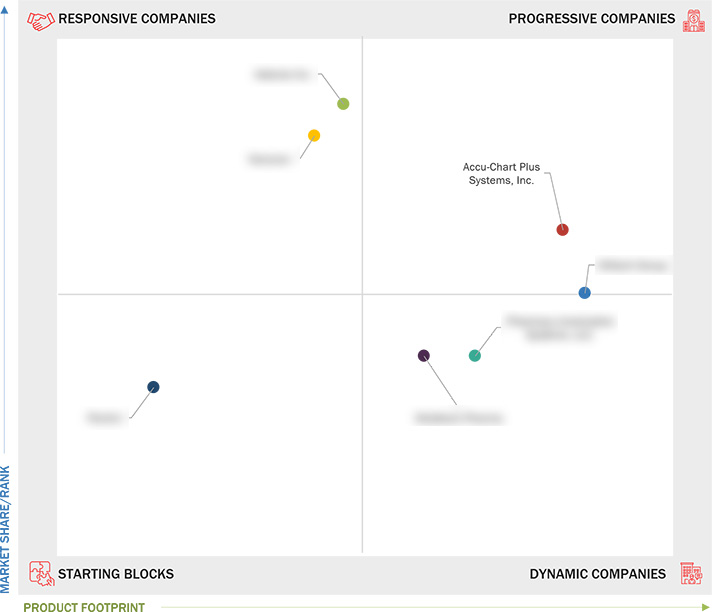
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Growing need to minimize medication errors
2.2.1.2 Decentralization of pharmacies
2.2.1.3 Rising geriatric population and subsequent uptake of automated dispensing systems
2.2.1.4 Growing focus on automation to reduce labor costs
2.2.1.5 Increasing demand for specialty drug dispensing
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 High initial capital investments
2.2.2.2 Reluctance to adopt pharmacy automation systems
2.2.2.3 Shortage of skilled personnel
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Gradual shift to online pharmacy services
2.2.3.2 Expansion of telepharmacy & remote patient management services
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Stringent regulatory process for automated pharmacy systems
2.2.4.2 Risk of cross-contamination
2.2.4.3 Technical failures and system reliability issues
2.2.4.4 Medication dispensing risks associated with drug name selections
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Product/Services Launches
3.8.2 Deals
3.8.3 Expansions
3.8.4 Other Developments
4.1 Wiilach Group
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 Accu-Chart Plus Health Care Systems, Inc.
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 Asteres Inc.
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 Newlcon
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 Pharmacy Automations Systems, LLC
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 Meditech Pharma
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 Plenful
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments