Comparing 5 vendors in Electronic Toll Collection Startups across 0 criteria.
The electronic toll collection (ETC) market focuses on automating toll payments on highways, bridges, and tunnels to reduce congestion and improve traffic flow. ETC systems eliminate the need for manual toll booths, offering faster and more efficient travel. These systems are increasingly adopted due to their convenience, fuel-saving benefits, and integration with intelligent transportation technologies. Governments and industries support ETC for its role in enhancing transportation infrastructure, streamlining operations, and promoting environmentally friendly commuting solutions.
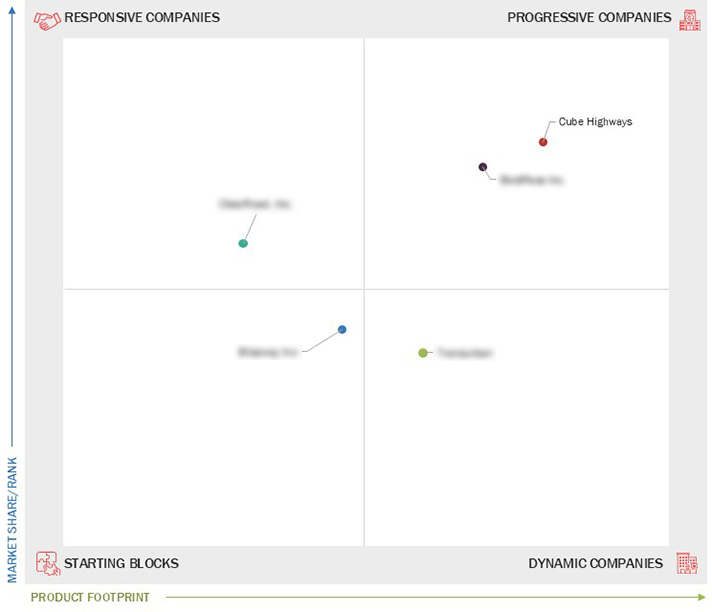
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Urgent need to mitigate traffic congestion and reduce road accidents
2.2.1.2 Strong government support to deploy advanced tolling solutions
2.2.1.3 High convenience of automated toll payment options
2.2.1.4 Technological advancements in transportation infrastructure
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Overreliance on technologies and susceptibility to technical failure
2.2.2.2 ETC implementation constraints in developing countries
2.2.2.3 Requirement for high initial investments in GPS- and GNSS-based ETC systems
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Significant focus on minimizing fuel consumption and emissions for economic and environmental gains
2.2.3.2 Integration of blockchain technology into toll collection systems
2.2.3.3 Rising number of public–private partnership agreements in transportation sector
2.2.3.4 Increasing adoption of all-electronic tolling systems
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Data privacy concerns
2.2.4.2 Interoperability issues associated with tolling systems
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Product Launches
3.8.2 Deals
3.8.3 Expansions
3.8.4 Other Developments
4.1 Cube Highways
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 BestPass Inc.
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 ClearRoad, Inc.
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 Blissway Inc
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 TRANSURBAN HOLDINGS LIMITED
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments