Comparing 10 vendors in Pressure Transmitter Startups across 0 criteria.
The pressure transmitter market, a crucial segment of the broader industrial and automation landscape, is poised for substantial growth from 2025 to 2030. This growth is driven by the increasing demand in various industries aiming to enhance production efficiency through enhanced process automation solutions. Pressure transmitters serve as an integral component in monitoring and controlling critical process parameters such as level, pressure, and flow, which are vital for maintaining safety and elevating productivity across diverse sectors.
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
1.8 Summary of Changes
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Rising use of Automation By Industry Players to Optimize Resources and Boost Efficiency
2.2.1.2 Increasing Implementation of IIoT and Industry
2.2.1.3 Growing Inclination of Manufacturing Firms Toward Real-time Analytics and Predictive Maintenance
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Requirement for Significant Investment and Technical Expertise
2.2.2.2 Need for Periodic Calibration of Pressure Transmitters to Ensure Precision
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Development of Pressure Transmitters with Smart Calibration and Self-Diagnostics Features
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Balancing Efficiency, Compatibility, and Sustainability in Pressure Transmitters in Rapid Digital Transformation
2.2.4.2 Providing Quick and Efficient Services Or Easy Replacement Solutions to Clients
2.2.4.3 Addressing Cybersecurity Risks Associated with IIoT Integration
2.3 Value Chain Analysis
2.4 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.7 Investment and Funding Scenario, 2019–2024
2.8 Technology Analysis
2.8.1 Key Technologies
2.8.1.1 Pressure Sensing Elements
2.8.1.2 Smart Calibration
2.8.1.3 Real-time Diagnostics
2.8.2 Adjacent Technologies
2.8.2.1 Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
2.8.2.2 AI-Powered Analytics
2.8.2.3 Wireless Communication Protocols
2.8.3 Complementary Technologies
2.8.3.1 Cloud Computing
2.8.3.2 Cybersecurity Solutions
2.9 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.9.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.9.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.9.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.9.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.9.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
2.12 Trade Analysis
2.12.1 Import Scenario (HS Code 902620)
2.12.2 Export Scenario (HS Code 902620)
2.13 Patents Analysis
2.14 Key Conferences and Events, 2025–2026
2.16 Impact of AI/Gen AI
2.16.1 Introduction
2.16.2 Impact of AI on Pressure Transmitter Market
2.16.3 Top Use Cases and Market Potential
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win, 2022–2024
3.3 Revenue Analysis, 2020–2024
3.4 Market Share Analysis, 2024
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics, 2025
3.6 Brand Comparison
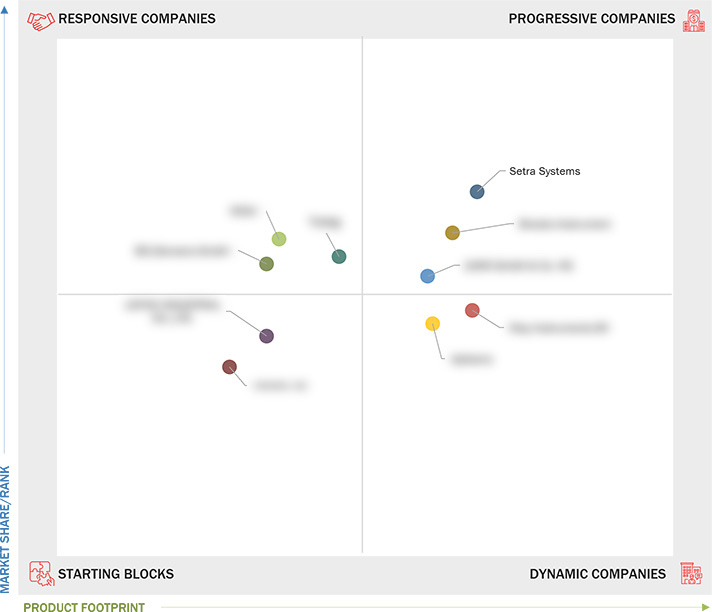
3.8 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs, 2024
3.8.1 Progressive Companies
3.8.2 Responsive Companies
3.8.3 Dynamic Companies
3.8.4 Starting Blocks
3.8.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs, 2024
3.8.5.1 Detailed List of Key Startups/SMEs
3.8.5.2 Competitive Benchmarking of Key Startups/SMEs
3.9 Competitive Scenario
3.9.1 Product Launches
3.9.2 Deals
3.9.3 Expansions
4.1 WIKA ALEXANDER WIEGAND SE & CO. KG
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 DWYER INSTRUMENTS, LLC.
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 VEGA
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 KELLER DRUCKMESSTECHNIK AG
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 HYDAC INTERNATIONAL GMBH
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 KLAY INSTRUMENTS
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 JUMO GMBH & CO. KG
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 BROOKS INSTRUMENT
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments
4.9 BD|SENSORS GMBH
4.9.1 Business overview
4.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.9.3 Recent developments
4.10 GEORGIN
4.10.1 Business overview
4.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.10.3 Recent developments
4.11 TRAFAG
4.11.1 Business overview
4.11.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.11.3 Recent developments
4.12 APLISENS S.A.
4.12.1 Business overview
4.12.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.12.3 Recent developments

 Totaljobs
Totaljobs
 Mar 2026
Mar 2026

