Comparing 4 vendors in Smart Glass Startups across 0 criteria.
Smart glass, also known as switchable, dimmable, or magic glass, can adjust the light transmission properties dynamically or statically, depending on the stimuli. The stimuli altering the light transmission properties could be light, voltage, or heat. It does not require electricity to maintain its opacity or change color. The installation of smart glass helps reduce the energy spent on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) and lighting systems and improves the indoor environmental quality of buildings.
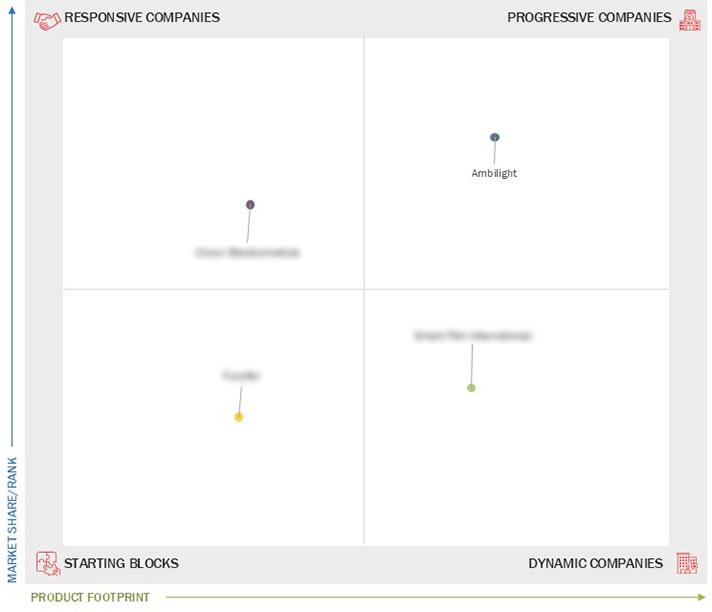
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Use of smart glass in modern luxury cars
2.2.1.2 Integration of electrochromic materials into smart glasses
2.2.1.3 Rising need to balance energy supply and demand
2.2.1.4 Emphasis on promoting low-carbon economy
2.2.1.5 Growing demand in construction and real estate sectors
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 High initial investments and upfront costs for implementing smart glasses
2.2.2.2 Operational and functional challenges related to smart glass technology
2.2.2.3 Complex manufacturing processes associated with smart glass
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Growing trend of minimalist designs
2.2.3.2 Increasing demand for alternative power sources due to rising energy costs
2.2.3.3 Rising emphasis on developing and commercializing smart glass technologies
2.2.3.4 Increasing demand for sustainable buildings
2.2.3.5 Growing demand for energy-efficient products
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Lack of awareness about long-term benefits of smart glass technology
2.2.4.2 Compliance with building codes and regulations
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Product Launches
3.8.2 Deals
3.8.3 Expansions
4.1 Ambilight
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 Crown Electrokinetics
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 Furcifer
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 Smart Film International
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments

 Stock Titan
Stock Titan
 Jan 2025
Jan 2025

