Comparing 10 vendors in Generative AI Cybersecurity Startups across 0 criteria.
Generative AI cybersecurity encompasses both the protection of generative AI systems and the transformative impact of these technologies on modern cybersecurity practices. The emergence of generative AI presents both opportunities and risks for cybersecurity. While it strengthens defensive capabilities, it also empowers attackers to create convincing deepfakes, sophisticated phishing campaigns, and automated cyberattacks. Recent cases reveal criminals using AI-generated voices for social engineering, resulting in major financial losses. Furthermore, as AI becomes more integrated into critical infrastructure and financial systems, risks such as AI model reverse engineering threaten to expose sensitive data and proprietary algorithms, underscoring the need for advanced, adaptive cybersecurity strategies. The widespread adoption of AI technologies has made robust cybersecurity measures essential to protect both AI systems and the sensitive data they handle. Industries such as healthcare and finance increasingly rely on AI for diagnostics, decision-making, and risk assessment, making them high-value targets for cyberattacks.
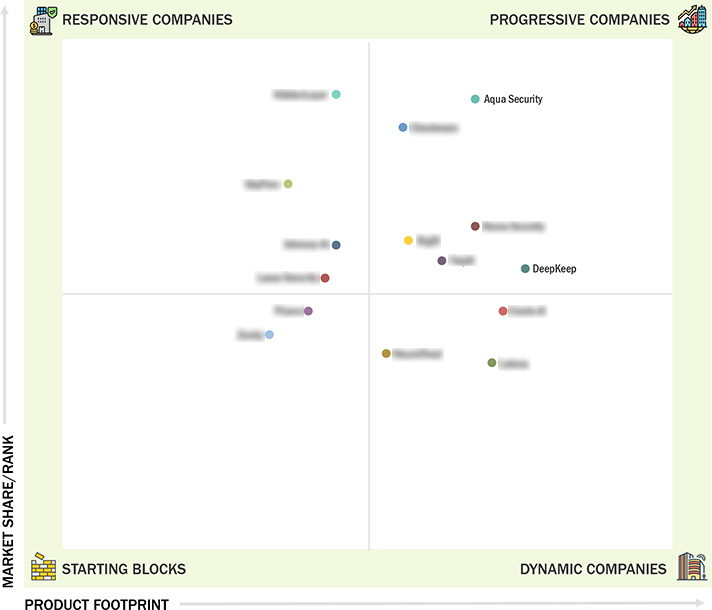
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Objectives of the Study
1.2 Market Definition and Scope
1.3 Market Scope
1.3.1 Market Segmentation
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Stakeholders
1.6 Summary of Changes
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Rising frequency and sophistication of AI-driven
cyberattacks
2.2.1.2 Operational efficiency gains through AI-assisted Security
Operations Centers (AI-SOC), reducing alert fatigue and
response times
2.2.1.3 Escalating zero-day vulnerabilities, necessitating rapid
AI-enabled detection and remediation
2.2.1.4 Growing demand for AI-powered behavioral anomaly detection
to combat insider threats
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Lack of standardized benchmarks for evaluation of AI
cybersecurity solutions
2.2.2.2 Uncertainty around liability in AI-led automated security
actions
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Adoption of Zero Trust for AI frameworks to validate AI-
generated outputs
2.2.3.2 Leveraging AI for real-time detection of adversarial AI
attacks on critical infrastructure
2.2.3.3 Development of AI-driven penetration testing and
vulnerability assessment platforms
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Exploitation of prompt injection and model manipulation
techniques to bypass safeguards
2.2.4.2 Proliferation of AI-enabled deepfake fraud targeting
enterprises and critical infrastructure
2.3 Evolution of Generative AI Cybersecurity
2.4 Supply Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.5.1 Generative AI-Based Cybersecurity Providers
2.5.2 Cybersecurity Providers for Generative AI
2.5.3 Generative AI Cybersecurity Service Providers
2.5.4 Security Types
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.1.1 Adversarial machine learning
2.7.1.2 Federated learning security
2.7.1.3 Differential privacy
2.7.1.4 Homomorphic encryption
2.7.1.5 Secure multi-party computation
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.2.1 Blockchain
2.7.2.2 Zero trust architecture
2.7.2.3 Endpoint detection & response
2.7.2.4 Vulnerability management
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.7.3.1 Quantum computing
2.7.3.2 DevSecOps
2.7.3.3 Forensics & incident response
2.7.3.4 Big data analytics
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.8.1 Methodology
2.8.2 Patents Filed, By Document Type
2.8.3 Innovation and Patent Applications
2.9 Key Conferences and Events (2025–2026)
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competition Rivalry
2.11 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
3.1 Overview
3.2 Key Player Strategies
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.4.1 Market Ranking Analysis
3.5 Product Comparative Analysis
3.6 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs, 2024
3.6.1 Startups/SMEs Offering Generative AI-Based Cybersecurity
3.6.1.1 Progressive companies
3.6.1.2 Responsive companies
3.6.1.3 Dynamic companies
3.6.1.4 Starting blocks
3.6.2 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs, 2024
3.6.2.1 Detailed List of Key Startups/SMEs
3.6.2.2 Competitive Benchmarking of Key Startups/SMEs
3.6.3 Startups/SMEs Offering Cybersecurity Solutions for Generative AI
3.6.3.1 Progressive companies
3.6.3.2 Responsive companies
3.6.3.3 Dynamic companies
3.6.3.4 Starting blocks
3.6.4 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs, 2024
3.6.4.1 Detailed List of Key Startups/SMEs
3.6.4.2 Competitive Benchmarking of Key Startups/SMEs
3.7 Competitive Scenario and Trends
3.7.1 Product Launches and Enhancements
3.7.2 Deals
4.1 AQUA SECURITY
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 BIGID
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 ADVERSA AI
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 CHECKMARX
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 CREDO AI
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 DEEPKEEP
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 LAKERA
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 SKYFLOW
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments
4.9 TROJAI
4.9.1 Business overview
4.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.9.3 Recent developments
4.10 NEURALTRUST
4.10.1 Business overview
4.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.10.3 Recent developments

 citybiz
citybiz
 Feb 2026
Feb 2026

