Comparing 9 vendors in Network Slicing Startups across 0 criteria.
Network slicing is a transformative approach in telecommunications that enables the creation of multiple virtual networks over a shared physical infrastructure. It allows service providers to deliver customized connectivity solutions tailored to specific business needs, offering benefits like low latency, high reliability, and scalability. This technology supports digital transformation by enabling flexible, secure, and efficient network services for mission-critical applications. Key drivers include the rise of private 5G, demand for real-time applications, and advancements in cloud-native and virtualized networking.
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Ultra-low latency slicing for real-time use cases
2.2.1.2 Rising enterprise demand for network customization
2.2.1.3 Private 5G adoption fueling slicing deployment
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Lack of unified standards across ecosystems
2.2.2.2 High cost of network transformation for smaller players
2.2.2.3 Security risks in multi-tenant environments
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 AI-powered orchestration for zero-touch slicing
2.2.3.2 Edge computing integration with slicing
2.2.3.3 Cross-industry co-development of slicing use cases
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 SLA enforcement remains difficult in live deployments
2.2.4.2 Shortage of slicing-skilled workforce
2.2.4.3 Operational complexity in managing multiple slices
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
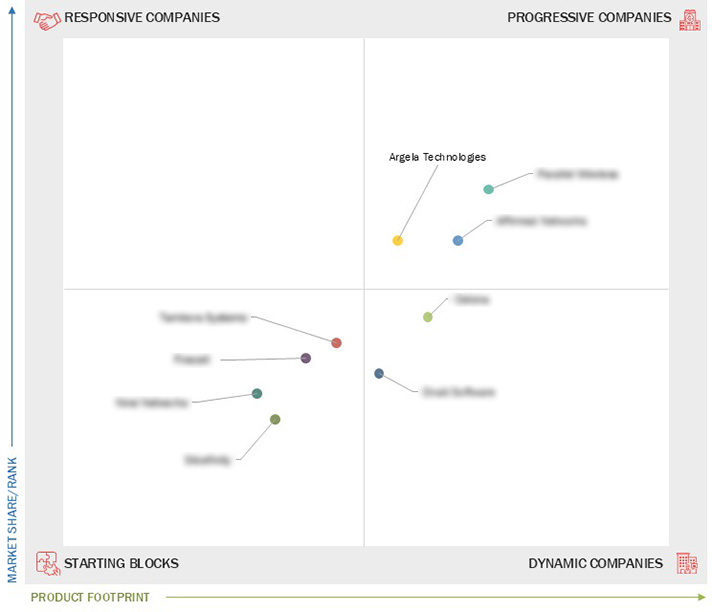
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Product Launches
3.8.2 Deals
4.1 Argela Technologies
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 Parallel Wireless
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 AFFIRMED NETWORKS
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 Celona
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 Druid Software
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 Tambora Systems
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 Firecell
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 Niral Networks
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments
4.9 SliceFinity
4.9.1 Business overview
4.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.9.3 Recent developments

 Hughes Network Systems, LLC
Hughes Network Systems, LLC
 Oct 2025
Oct 2025

