Comparing 8 vendors in Smart Cities Startups across 0 criteria.
Smart cities are transforming urban life by integrating advanced technologies to improve public services, sustainability, and governance. These cities use real-time data, intelligent infrastructure, and digital platforms to enhance efficiency and quality of life. Key innovations include smart transportation, energy grids, buildings, and citizen services. Technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing enable seamless operations and better resource management. Despite challenges like high costs and data security, smart cities offer promising solutions for urban resilience and inclusive development.
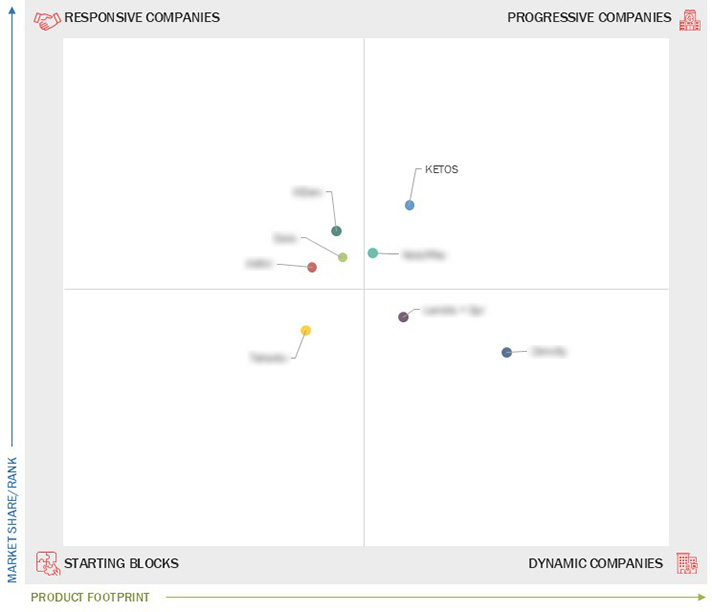
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.3.3 Years Considered
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in urban development
2.2.1.2 Growing urbanization across regions
2.2.1.3 Need for efficient management and utilization of resources
2.2.1.4 Demand for fast and efficient transport
2.2.1.5 Surveillance in interest of public safety
2.2.1.6 Need for healthy environment with efficient energy consumption
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 Privacy and security concerns
2.2.2.2 High cost of implementation
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Advancements in AI, cloud, IoT, and analytics technologies
2.2.3.2 Rise of 5G technology
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Achieving future-readiness of smart cities for sustainable urban living
2.2.4.2 Absence of suitable infrastructure in emerging economies
2.2.4.3 Limited awareness among people about smart cities
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Value Chain Analysis
2.5 Ecosystem Analysis
2.6 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.8 Patent Analysis
2.9 Trade Analysis
2.10 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.10.1 Threat of New Entrants
2.10.2 Threat of Substitutes
2.10.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.10.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.10.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win
3.3 Revenue Analysis
3.4 Market Share Analysis
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics
3.6 Brand/Product Comparison
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Product Launches
3.8.2 Deals
3.8.3 Others
4.1 Appyway
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 GAIA
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 INRIX INC
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 IXDen
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 KETOS
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 Landys + Gyr
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 TAKADU
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 ZENCITY
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments

 SmartCitiesWorld
SmartCitiesWorld
 Jun 2024
Jun 2024

