Comparing 5 vendors in Smart Meter Startups across 0 criteria.
The global smart meter market represents a significant leap in utility management, merging advanced technology and innovative solutions to address contemporary energy and resource challenges. Smart meters transform the traditional utility landscape, allowing for automated data acquisition, precise monitoring, and efficient electricity, gas, and water consumption management. Through these technologies, utility providers can engage in two-way communication, optimize billing processes, enhance customer service, and improve asset management.
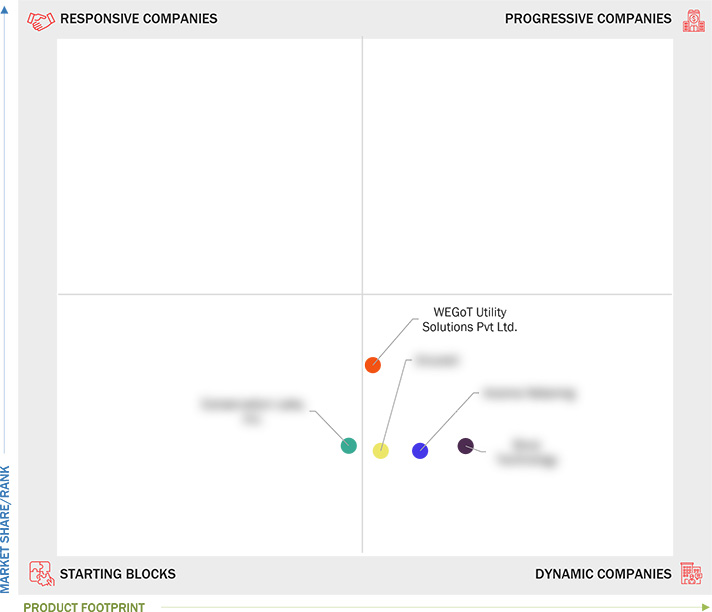
Market Leadership Quadrant
1.1 Study Objectives
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Study Scope
1.3.1 Markets Covered and Regional Scope
1.3.2 Years Considered
1.3.3 Inclusions and Exclusions
1.4 Currency Considered
1.5 Unit Considered
1.6 Limitations
1.7 Stakeholders
1.8 Summary of Changes
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Market Dynamics
2.2.1 Drivers
2.2.1.1 Government focus on modernizing grid infrastructure
2.2.1.2 Greater emphasis on cutting energy bills by monitoring real-time consumption
2.2.1.3 Dynamic electricity pricing
2.2.1.4 High adoption of preventive measures against grid blackouts and utility system failures
2.2.1.5 Increased need to monitor energy consumption to achieve carbon neutrality
2.2.2 Restraints
2.2.2.1 High setup and operational costs, coupled with interoperability issues
2.2.2.2 Concerns related to consumer acceptance and ROI delays
2.2.3 Opportunities
2.2.3.1 Pressing need to reduce non-revenue water losses
2.2.3.2 Focus of governments worldwide on reducing aggregate technical and commercial losses in power grids
2.2.3.3 Integration of AI and ML technologies into smart meters
2.2.3.4 Rising adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles
2.2.3.5 Increasing focus of developing countries on improving water distribution networks
2.2.4 Challenges
2.2.4.1 Requirement for highly skilled professionals, coupled with data privacy and security concerns
2.2.4.2 Complexities in building reliable connections between smart meters and smart grid devices
2.3 Trends/Disruptions Impacting Customer Business
2.4 Industry Trends
2.5 Value Chain Analysis
2.6 Ecosystem Analysis
2.7 Technology Analysis
2.7.1 Key Technologies
2.7.1.1 Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI)
2.7.1.2 Virtual time of Use (VTOU)
2.7.2 Complementary Technologies
2.7.2.1 Home energy management systems (HEMS)
2.7.3 Adjacent Technologies
2.7.3.1 Smart grid
2.7.3.2 Cybersecurity solutions for smart meters
2.8 Patent Landscape
2.9 Patent Analysis
2.10 Trade Analysis
2.10.1 Export Scenario (HS Code 9028)
2.10.2 Import Scenario (HS Code 9028)
2.11 Key Conferences and Events, 2025
2.12 Regulatory and Policy Framework
2.13 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.13.1 Threat of Substitutes
2.13.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
2.13.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
2.13.4 Threat of New Entrants
2.13.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
2.14 Pricing and Cost Analysis
2.15 Investment and Funding Scenario
2.16 Impact of Gen AI/AI on Smart Meter Market
2.16.1 Adoption of Gen AI/AI for Smart Meter Applications
2.16.2 Impact of Gen AI/AI on Smart Meter Supply Chain, By Region
2.17 Global Macroeconomic Outlook
2.17.1 Introduction
2.17.2 Rise in Smart Grid Investments Worldwide
2.17.3 Technological Advancements
2.17.4 Government Support and Regulatory Mandates
2.17.5 Strong Focus of Consumers on Adopting Energy-Efficient Products
3.1 Overview
3.2 Key Player Strategies/Right to Win, 2020–2025
3.3 Market Share Analysis, 2023
3.4 Revenue Analysis, 2019–2023
3.5 Company Valuation and Financial Metrics, 2025
3.6 Product Comparison
3.7 Company Evaluation Matrix: Startups/SMEs, 2023
3.7.1 Progressive Companies
3.7.2 Responsive Companies
3.7.3 Dynamic Companies
3.7.4 Starting Blocks
3.7.5 Competitive Benchmarking: Startups/SMEs, 2023
3.7.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
3.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
3.8 Competitive Scenario
3.8.1 Product Launches
3.8.2 Deals
3.8.3 Expansions
3.8.4 Other Developments
4.1 Other Players
4.1.1 Business overview
4.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.1.3 Recent developments
4.2 JIANGSU LINYANG ELECTRONICS
4.2.1 Business overview
4.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.2.3 Recent developments
4.3 HEXING ELECTRICAL CO. LTD.
4.3.1 Business overview
4.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.3.3 Recent developments
4.4 NETWORKED ENERGY SERVICES
4.4.1 Business overview
4.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.4.3 Recent developments
4.5 PIETRO FIORENTINI S.P.A.
4.5.1 Business overview
4.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.5.3 Recent developments
4.6 SECURE METERS LTD.
4.6.1 Business overview
4.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.6.3 Recent developments
4.7 WEGOT UTILITY SOLUTIONS PVT LTD.
4.7.1 Business overview
4.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.7.3 Recent developments
4.8 AXIOMA METERING
4.8.1 Business overview
4.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.8.3 Recent developments
4.9 DRIZZLEX, INC.
4.9.1 Business overview
4.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.9.3 Recent developments
4.10 CONSERVATION LABS, INC.
4.10.1 Business overview
4.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.10.3 Recent developments
4.11 BOVE TECHNOLOGY
4.11.1 Business overview
4.11.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
4.11.3 Recent developments

 Smart Energy International
Smart Energy International
 May 2025
May 2025

